Uncategorized
Restricting and Excluding
The Big Six Pathogens
Time-Temperature Abuse
Food Storage
Personal Hygiene
Lesson 1
Lesson 2
Lesson 3
Lesson 4
Lesson 5
Lesson 6
Lesson 7
Lesson 8
Module Nine
Lesson 10
Section II
Wrong shortcode initialized
Section I
Wrong shortcode initialized
Section I
Wrong shortcode initialized
Section Ten
Why you should NOT wash raw chicken before cooking.

Raw chicken is gross, why shouldn’t I wash it?
Raw chicken from the grocery store looks and feels gross. The skin has little bumps and feels wet and clammy. There are red and yellowish juices throughout the packaging and dripping from the bird, disgusting!
Not only that, but we have all heard horror stories about how nasty a meat processing plant can be. Or the industrial farms where chickens are raised – crammed in tiny cages and wallowing their own filth, yuck!
If you have a little more knowledge about food safety, you may still be convinced that poultry needs to be washed before cooking. After all, poultry is one of the biggest carriers of the pathogens that cause foodborne illness. This is why poultry needs to be cooked to a higher temperature than foods (165°F) in order to make it safe to eat. It makes sense that rinsing the bird first is an extra precaution against illness.
And some of us have memories of our mothers or grandmothers giving the bird a quick rinse in the sink before seasoning or carving it. And it seems like a good idea so we pass that “wisdom” on to our children. But unfortunately, washing poultry does more harm than good. So why is it dangerous to wash chicken before cooking it?
Because washing raw chicken makes an even bigger mess!
The water used to wash the chicken splashes everywhere, even if it doesn’t seem like it. One little splash can cause tiny water droplets to fly up to two feet in any direction.
Then the juices are on your hands and you touch the faucet to turn it off. After that, you may wipe your hands on a towel making it contaminated too.
Now the chicken juices are all over the sink, faucet, counter, towels and you! Your kitchen is entirely contaminated.
Raw poultry, and especially chicken contain a pathogen called campylobacter. And campylobacter is the leading cause of foodborne illness in the United States. It only takes one microscopic campylobacter organism on your counter to quickly multiply into millions and billions of campylobacter organisms.
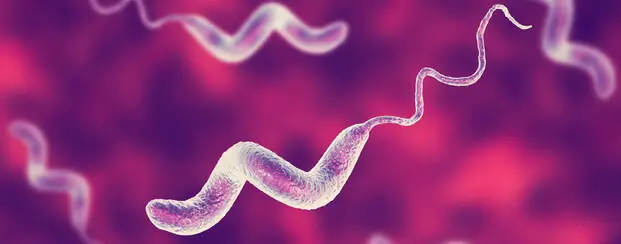
If enough campylobacter is accidentally ingested or enters the body through hand to mouth contact, a person can become sick. And in some cases, the sickness can even lead to death.
If there are young children in the house then the scenario becomes even worse. Preschool-age children are very susceptible to foodborne illness because their bodies have not yet developed a strong enough immune system. Also, the elderly and people who are already sick with other diseases are more susceptible as well.

There have always been two sides to the argument and everyone has an opinion. But there is only one correct answer, you should not wash raw poultry before cooking it. Now that you know the reason it’s quite simple and easy to understand – explain it to others so that they know it too.
As long as you cook poultry to the correct internal temperature, it becomes totally safe to eat.
TAP Series
What is TAP Series?
TAP Series leads the industry in online courses and cloud solutions for the foodservice industry. Their primary focus is food manager and food handler training. Hundreds of thousands have passed the Food Safety Manager exam when using TAP to prepare for the Food Safety Manager exam.
TAP Series is the most recognized Food Safety Manager Course in the country by striving to provide the most effective and efficient Food Safety Manager exam prep materials. TAP Series has trained over 500,000 Food Handlers nationwide with more being trained every day.
Online food safety course for food manager certification
There are some things to keep in mind before choosing to take the online course. You will have to find a certified proctor to administer the exam; you’re not allowed to take the exam alone. You can find a directory of proctors by hovering over the ServSafe® Testing tab.
ServSafe Food Protection Manager Exam
An Exam Proctor will need to be physically present to administer an exam.
We offer exams at these locations at 3:30 pm on the date of scheduled classes. More locations can be found by hovering over the “ServSafe® Testing” tab located on the top menu bar.
Exams will be administered online and are available in English, Spanish or Chinese unless otherwise requested.
Print exams may be requested in English, Spanish, French Canadian, Japanese, Korean, Chinese or Large Print 15 days in advance and will incur an additional charge of $15.00 billed separately for shipping & handling. Exam results will be available in 10 business days.
Choosing an online food safety course
We offer both ServSafe® and TAP Series® food safety courses for managers. We highly recommend the TAP Series course for several reasons which are outlined below. Some people still choose ServSafe because of name recognition. It’s a personal preference so we provide both.
Both food safety courses are nationally accredited and provide the same curriculum. Students pass the exam at the same rate with both courses. But TAP Series is more affordable and offers a few extra perks that ServSafe doesn’t. With TAP Series you have immediate access to your course and they provide 24-hour support. ServSafe only provides support between 8 am and 6 pm. Also, TAP Series is the only food safety course with a training warranty and they offer refunds in limited situations.
Both food safety courses can result in a ServSafe® certificate
Both the ServSafe and TAP Series food safety courses can result in a ServSafe certificate. This is because your certificate is awarded according to which exam you pass; not which course you complete. You do not have to take the ServSafe course in order to take their exam. The Hospitality Training Center only administers ServSafe exams and we will provide the exam regardless of which course you’ve completed. We take the exam online so that your results and a valid ServSafe certificate can be available immediately after the session has completed.
